Second Derivative Calculator
Calculate second derivatives step by step
This calculator will find the second derivative of any function, with steps shown. Also, it will evaluate the second derivative at the given point if needed.
Related calculators: Derivative Calculator, Logarithmic Differentiation Calculator
The Second Derivative Calculator will calculate the second derivative of a function. The step-by-step solutions it provides help deepen the knowledge of the second derivative, which provides information about the concavity of the function's curve and its inflection points.
How to Use the Second Derivative Calculator?
Input
Enter the function you want to differentiate twice.
Calculation
Click the "Calculate" button.
Result
Use the resulting second derivative to find the function's inflection points and intervals of concavity.
What Is the Second Derivative?
The second derivative is the derivative of the first derivative of a function. It is also an important concept in calculus, which provides insight into the concavity of functions.
Notation
For a given function $$$f(x)$$$:
- The first derivative, denoted as $$$f^{\prime}(x)$$$, represents the rate of change of $$$f(x)$$$.
- The second derivative, denoted as $$$f^{\prime\prime}(x)$$$, represents the rate of change of $$$f^{\prime}(x)$$$: $$$f^{\prime\prime}(x)=\left(f^{\prime}(x)\right)^{\prime}$$$.
Concavity
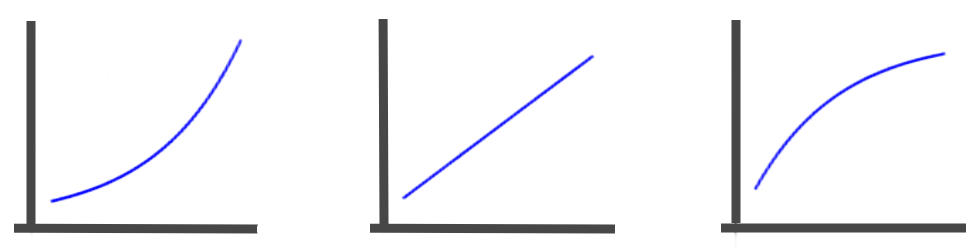
The second derivative gives information about the concavity of the function's curve:
- If $$$f^{\prime\prime}(x)\gt0$$$ on some interval, the function is concave upwards on that interval.
- If $$$f^{\prime\prime}(x)\lt0$$$ on some interval, the function is concave downwards on that interval.
Inflection Points
An inflection point is a point where the concavity of the function changes. Mathematically, it's a point where:
- $$$f^{\prime\prime}(x)=0$$$ or $$$f^{\prime\prime}(x)$$$ is undefined.
- The sign of $$$f^{\prime\prime}(x)$$$ changes at that point.
Example
Suppose we are given the function $$$y=x^3+2x^2+6x+5$$$:
- First Derivative: $$$f^{\prime}(x)=3x^2+4x+6$$$.
- Second Derivative: $$$f^{\prime\prime}(x)=(3x^2+4x+6)^{\prime}=6x+4$$$.
Therefore, the function is concave upwards when $$$6x+4\gt0$$$ or $$$x\gt-\frac{2}{3}$$$, concave downwards when $$$6x+4\lt0$$$ or $$$x\lt-\frac{2}{3}$$$, and has one inflection point at $$$x=-\frac{2}{3}$$$.
Second Derivative Test for Local Extrema
In calculus, the second derivative test is a valuable tool that helps determine the nature of the critical or stationary points of a function, in particular, whether these points are local maxima, local minima, or neither. The test uses the second derivative to determine the concavity of the function at these points.
Given a function $$$f(x)$$$ with a critical point at $$$x=c$$$:
- If $$$f^{\prime\prime}(x)\gt0$$$, then $$$x=c$$$ is a local minimum because the function $$$f(x)$$$ is concave upwards at this point. This means that, in a small neighborhood of $$$x=c$$$, the function values are greater than $$$f(c)$$$.
- If $$$f^{\prime\prime}(x)\lt0$$$, then $$$x=c$$$ is a local maximum because the function $$$f(x)$$$ is concave downwards at this point. This means that, in a small neighborhood of $$$x=c$$$, the function values are less than $$$f(c)$$$.
- If $$$f^{\prime\prime}(x)=0$$$ or $$$f^{\prime\prime}(x)$$$ does not exist, the second derivative test is inconclusive. The point can be an inflection point, a local maximum, a local minimum, or none of the above. In such cases, further analysis or other methods are needed to determine the nature of the critical point.
Why Choose Our Second Derivative Calculator?
Precision
The calculator provides high accuracy, removing the possibility of human errors that can occur with manual calculations.
Speed
Our tool produces instant results. No more lengthy manual calculations. You save your time.
Intuitive Design
Navigating our calculator is a breeze thanks to its user-friendly interface, which is designed to simplify the entire process.
Versatility
Our calculator can handle a wide range of functions, from trigonometric to logarithmic.
FAQ
What is the second derivative?
The second derivative of a function is the rate of change of its first derivative. For a function $$$f(x)$$$, its second derivative is denoted by $$$f^{\prime\prime}(x)$$$.
When is the second derivative positive?
If the second derivative $$$f^{\prime\prime}(x)$$$ is positive at some point or on some interval, the function $$$f(x)$$$ is concave upwards at that point or on that interval.
What is the second derivative test used for?
The second derivative test is a method used to determine the nature of critical points (where the first derivative is zero or undefined) of a function. If $$$f^{\prime\prime}(c)\gt0$$$, the function has a local minimum at $$$x=c$$$. If $$$f^{\prime\prime}(c)\lt0$$$, there is a local maximum at $$$x=c$$$. If $$$f^{\prime\prime}(c)=0$$$, the test is inconclusive, and other methods are needed to determine the nature of the critical point.
What does the Second Derivative Calculator do?
The Second Derivative Calculator is a tool that computes the second derivative of a function. It provides fast and accurate results without the need for manual calculations.
